Dry Skin Love Skincare
Protect Your Skin Barrier
How to protect you skin barrier
Protect Your Skin Barrier
Your Skin Barrier Protects You
Your skin barrier is what you can see and touch on the surface of your body

Protect Your Skin Barrier
What is Your Skin Barrier?
Your skin barrier includes the outermost layers of skin, called the stratum corneum.
When your skin barrier is healthy, it feels and appears smooth, soft, and plump.
In contrast, a damaged skin barrier looks dry, rough, dull, and dehydrated, and may become irritated and inflamed.
Your skin barrier includes:
- The acid mantle
- The lipid barrier
- The moisture barrier
- The protein barrier
Protect Your Skin Barrier
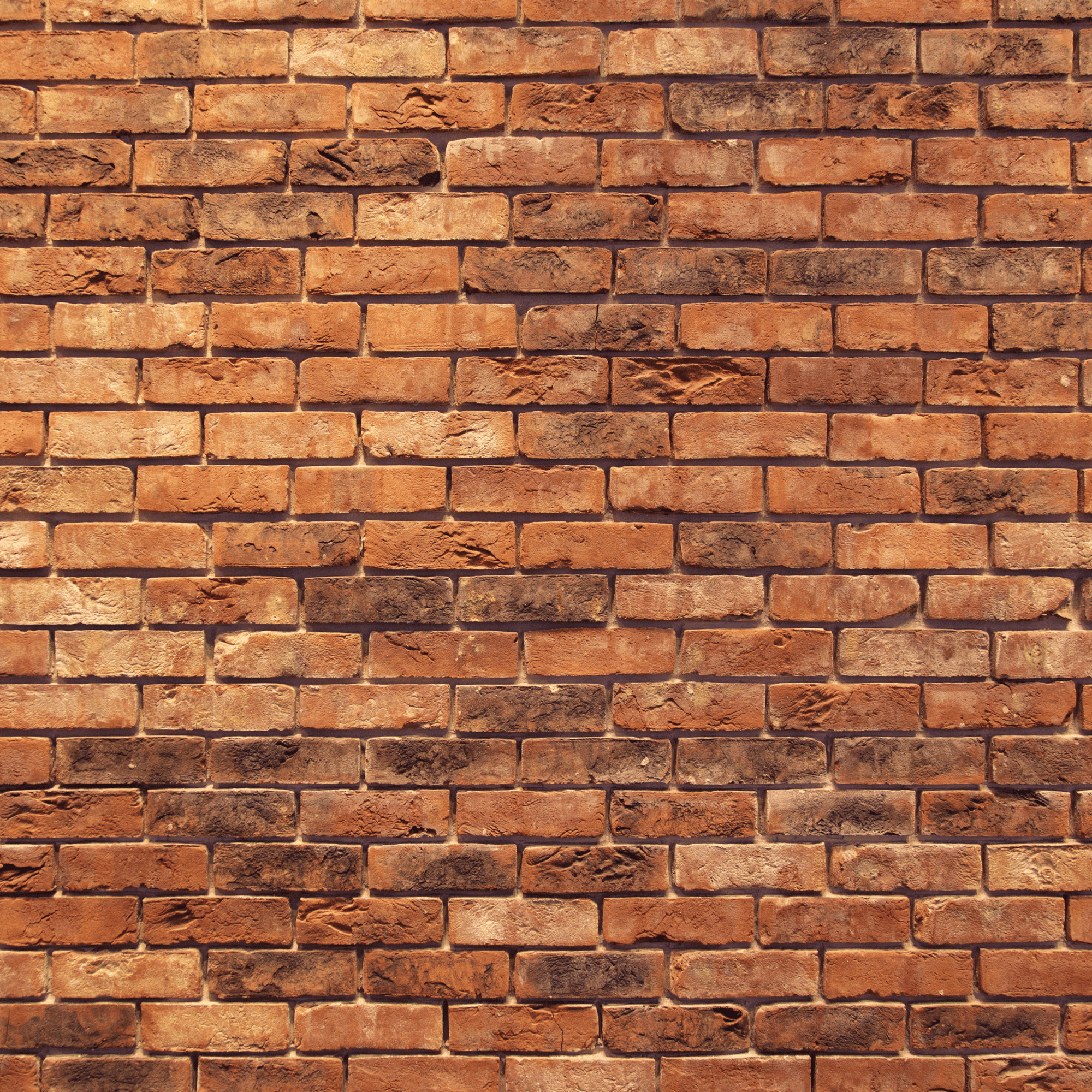
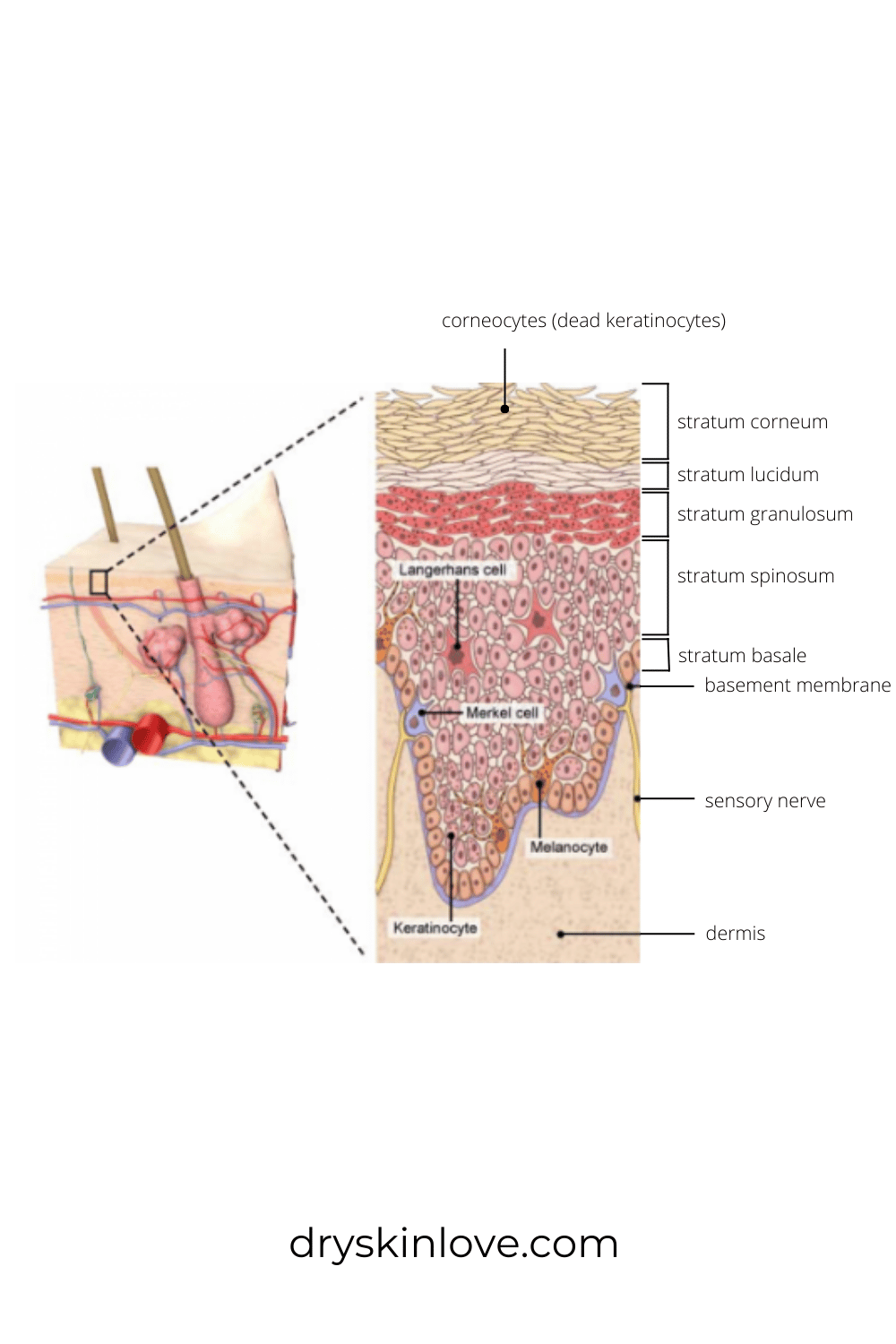
Stratum Corneum is a Brick Wall that Protects You
Your stratum corneum is the most outer layer of your skin.
The stratum corneum can be thought of as a brick wall that protects you.
The "bricks" are your skin cells, called corneocytes, and the "mortar" that holds the bricks together is the lipids or fats, that together create the outer barrier.
On a weight basis, the stratum corneum contains approximately 70% protein, 15-25% water and 15% lipids.

Protect Your Skin Barrier
Cell Turnover and Loss
Desquamation is the natural process of shedding your skin cells.
There are 15 to 30 layers of bricks (corneocytes) in the outer wall (stratum corneum).
Corneocytes are matured from skin cells called keratinocytes, which populate the lower levels of the skin barrier.
New skin cells are formed at the base layer of the skin, and they differentiate and migrate towards the skin surface, in a process that takes approximately 30 days.
Nearly a billion cells are lost each day from the surface of adult skin.
Protect Your Skin Barrier
Your Protein Barrier
Your protein barrier is a part of your skin barrier

Protect Your Skin Barrier
Your Protein Barrier
The protein layer is critical for the skin’s structural integrity, made of proteins like collagen, elastin, and keratin.
It helps maintain firmness, smoothness, and elasticity, and supports the skin’s overall strength.
Corneocytes are mostly made up of the protein keratin, which is also found in hair and nails.
Corneocytes in the stratum corneum are filled with keratin filaments as well as amino acids (AAs) and other small molecules, collectively referred to as natural moisturizing factors (NMFs), derived from the breakdown of filaggrin, a protein that surrounds the keratin filaments.
Protect Your Skin Barrier
Your Lipid Barrier
Your lipid barrier is a part of your skin barrier
Protect Your Skin Barrier
What is Your Skin's Lipid Barrier?
The surface of your skin is covered by a layer of protective fats, including epidermal lipids and sebum.
Epidermal lipids include:
- Ceramides
- Free fatty acids
- Cholesterol
Sebum is made of:
- Triglycerides
- Wax esters
- Squalene
Theses beneficial fats and lipids are naturally found in the lipid barrier and skin barrier and play a critical role in keeping your skin healthy.


Protect Your Skin Barrier
How To Protect Your Skin's Lipid Barrier
The surface of your skin is covered by a layer of beneficial fats, including epidermal lipids and sebum.
These natural fats and lipids help to lubricate and coat your skin cells and nourish your skin.
To protect your lipid barrier:
- Use emollients for dry skin
- Use carrier oils for dry skin
- Use linoleic acid for dry skin
Protect Your Skin Barrier
Your Moisture Barrier
Your moisture barrier is a part of your skin barrier
Protect Your Skin Barrier
What is Your Skin's Moisture Barrier?
Water is essential for the normal functioning of the skin.
The skin's moisture barrier ensures your skin is hydrated by trapping and holding water into your skin.
The skin's moisture barrier is composed of water, natural moisturizing factors (NMFs) and other humectants, such as glycerol and hyaluronic acid to attract and hold onto moisture.
The water content of skin is remarkably high - the epidermis contains more than 70% water, while its outermost layer, the stratum corneum has been shown to contain ~ 25% water.
Adequate hydration of the stratum corneum serves three major functions:
1- it maintains plasticity of the skin, protecting it from damage
2- it contributes to optimum stratum corneum barrier function
3- it allows hydrolytic enzymes to function in the process of desquamation
When the water content of the stratum corneum falls below 10%, scaling on the skin surface becomes visible.
Protect Your Skin Barrier
How To Protect Your Skin's Moisture Barrier
To prevent dry or dehydrated skin, you must protect your skin barrier, including your skin's moisture barrier.
To protect your moisture barrier:
- Drink adequate water and fluids
- Use a humidifier
- Use a moisturizer with humectants
- Limit exposure to cold weather
- Protect your skin from the wind and sun
- Wear sunscreen and sunblock to protect against sun exposure

Protect Your Skin Barrier
Your Acid Mantle
Your acid mantle is a part of your skin barrier

Protect Your Skin Barrier
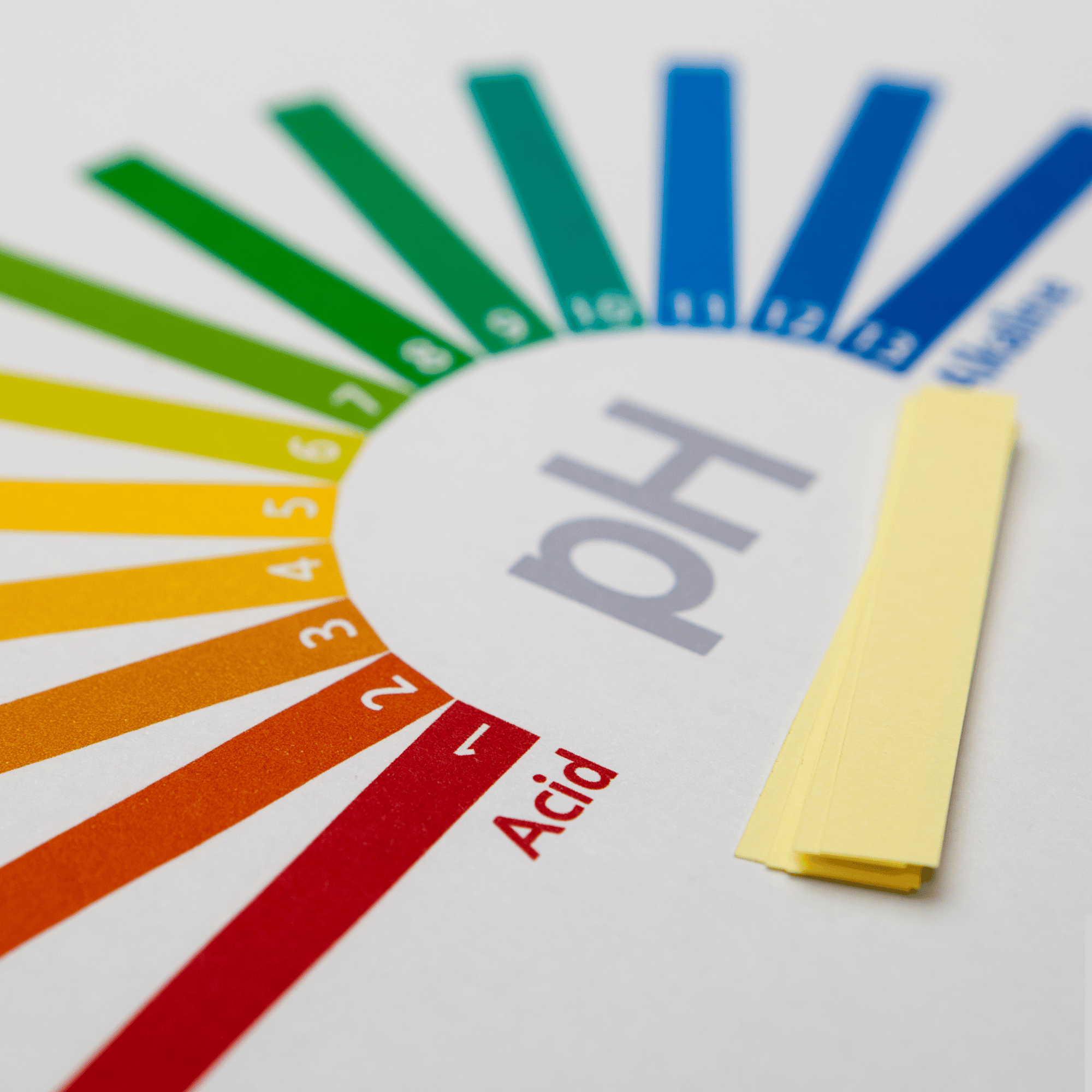
What is Your Skin's Acid Mantle?
Your skin's acid mantle describes the inherent acidic nature of the outer skin barrier, also known as the stratum corneum.
The pH of the skin barrier is slightly acidic, in the range 4.5 to 6.5.
Your skin pH influences:
- Skin barrier function
- Desquamation or shedding of skin cells
- Protection against pathogens "bad bacteria"
A proper skin pH is important to maintain healthy skin.
Protect Your Skin Barrier
How To Protect Your Skin's Acid Mantle
Many factors can affect the pH of the skin, including aging, sebum, sweat, detergents, cosmetics, and irritation.
Soaps and cleansers that are high in pH should be avoided, as high pH soaps can irritate and disrupt the skin barrier.
How to protect your skin's acid mantle:
- Avoid high pH soaps
- Use a gentle cleanser
- Try an oil cleanser
A proper skin pH is important to maintain healthy skin.


Protect Your Skin Barrier
Protect Your Skin Barrier
To prevent dry skin, you must protect your skin barrier, including your skin's moisture barrier, lipid barrier and acid mantle.
To protect you skin's moisture barrier, drink water, use a humidifier, use a moisturizer with humectants. protect your skin from wind, cold weather and sun exposure, and always wear sunscreen or sunblock, especially when you go outside.
To protect your lipid barrier, use emollients for dry skin such as carrier oils rich in linoleic acid.
To protect your skin's acid mantle avoid high pH soaps, use a gentle cleanser and try an oil cleanser.





