

BEST SKIN CARE FOR AGING SKIN
Dry Skin Love Pineapple 10% Vitamin C Face Oil for Aging Skin
Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
Dry Skin Love Pineapple 10% Vitamin C Face Oil is a unique formula that revitalizes and brightens aging skin.
This luxurious face oil will brighten your complexion, diminish the appearance of age spots and discoloration, and unveil a more luminous skin tone.
Made with gentle vitamin C ester tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate (THDA).
Created by scientist Dr. Natasha Ryz
Size = 50 ml / 1.76 oz
Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
Anti-Aging Benefits
"The pineapple face oil is a powerful anti-aging treat for dry skin. This beautiful face oil combines pineapple seed oil with 10% tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate - a gentle vitamin C ester with many benefits. It can reduce the appearance of age spots and fine lines. Makes your dry skin appear soft, plump and bright."
- Dr. Natasha Ryz, PhD
Founder Dry Skin Love Skincare

Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
Benefits for Your Skin
Bright, luminous and youthful.
Transform your mature skin with Dry Skin Love Pineapple 10% Vitamin C Face Oil, a luxurious formula designed to brighten and revitalize.
Formulated with tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate, a gentle vitamin C ester, this face oil targets age spots and discoloration, revealing a more even and radiant complexion. Infused with pineapple seed oil, it nourishes your skin while enhancing its natural glow.
Regular use helps diminish the appearance of fine lines, promoting a youthful and luminous skin tone.
Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
So Many Compliments!
"I live in Winnipeg, Manitoba and have been using the pineapple oil for the last month. My skin has never been more moisturized. After using the oil, I haven’t been applying makeup and have gotten so many compliments on my skin. It looks plumper, more vibrant and feels very soft. My husband who frequently gets red patches on his face close to his nose started using it and within days the redness was gone. The smell is heavenly, as are all of Dr. Ryz’s products. Applying the face oil is a pleasant, comforting moment of my day that I look forward to and enjoy. Great product!"
Barbara M.
Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada
Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
Directions for Use
For best results, apply the Pineapple Vitamin C Face Oil to clean dry skin.
- Apply a few drops of face oil into your clean hands.
- Gently rub face oil together in your hands and then apply face oil onto your face and neck.
- Gently massage into your face and neck until face oil is absorbed.
- All a few minutes for any excess face oil to absorb.
- If you add too much face oil, simply dab off excess with a clean tissue.
- Enjoy your soft, nourished and protected skin.

Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
Fantastic!
"Love the new Pineapple Face Oil! My face is brighter and softer with just a small amount of the product. Perfect to use after the the Wild Orange Cleanser."
Gloria R.
Ochre River, Manitoba, Canada
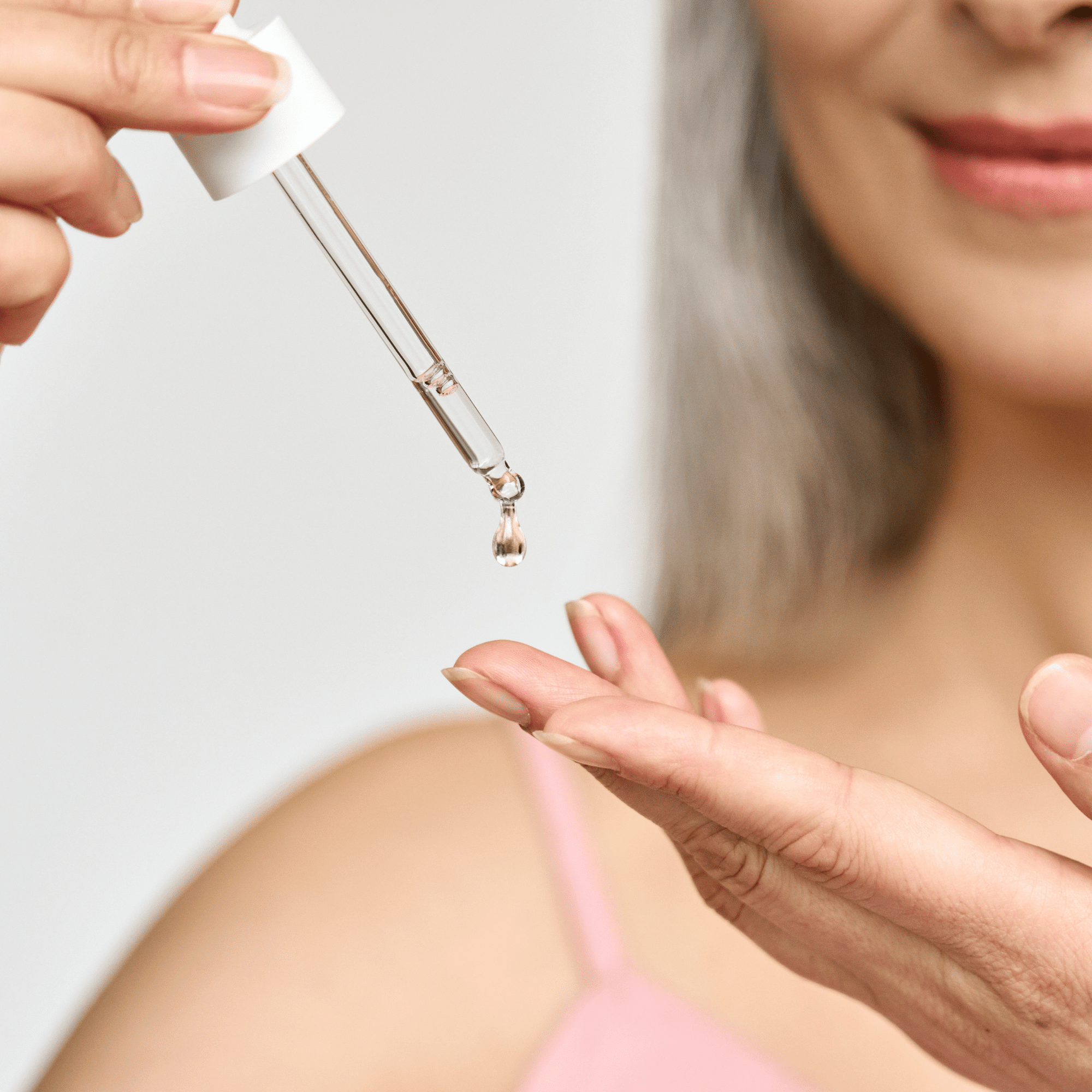
Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
What is Vitamin C?
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant found naturally in your skin.
As you age, your skin has lower levels of vitamin C.
Exposure to sunlight and UV irradiation as well as smoking can deplete vitamin C levels in your skin.
Topically applied vitamin C can help replenish your skin's vitamin C levels.
Topical vitamin C has benefits for your skin.
Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
Vitamin C Ester Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate
Have you been wanting to try vitamin C, but your dry skin gets irritated with ascorbic acid?
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate (THDA) is a gentle, stable and effective vitamin C ester.
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate has emollient properties, which means it can help moisturize and nourish your dry skin.
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate has clinically been shown to improve skin texture, brighten skin and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate is generally well-tolerated by various skin types, including dry and sensitive skin.


Best Vitamin C for Mature Skin
Premium Ingredients
Dry Skin Love Pineapple 10% Vitamin C Face Oil is made with premium ingredients, including cold-pressed pineapple seed oil and gentle vitamin C ester tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate (THDA).
We choose natural plant ingredients that are minimally processed and unrefined so they retain their nutrients, color and aromatic compounds.
We put incredible thought and effort into sourcing our precious ingredients for our luxurious face oil.
Every single ingredient has multiple benefits for your skin.
Dry Skin Love Pineapple 10% Vitamin C Face Oil for Aging Skin
Full Ingredients
Ananas comosus (Pineapple) seed oil¹, Cocos nucifera (Extra Virgin Coconut) oil*¹, Simmondsia chinensis (Golden Jojoba) oil*¹, Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate (Vitamin C ester), Polyglyceryl-4 Oleate, Vitamin E tocopherols from Glycine max extract, Matricaria recutita L. (Chamomile) flower extract*, Vanilla planifolia (Vanilla) extract*
*Certified Organic Ingredients
¹Cold Pressed Oil
Polyglyceryl-4 oleate is a natural emulsifier made from sunflower seed oil and vegetable glycerin.





